Difference between revisions of "Bakossi National Park"
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Central Africa]] > [[Cameroon]] > [[Bakossi National Park]] | [[Central Africa]] > [[Cameroon]] > [[Bakossi National Park]] | ||
| − | = | + | '''[https://wiki-iucnapesportal-org.translate.goog/index.php/Bakossi_National_Park?_x_tr_sl=auto&_x_tr_tl=fr&_x_tr_hl=en&_x_tr_pto=wapp Français]''' | '''[https://wiki-iucnapesportal-org.translate.goog/index.php/Bakossi_National_Park?_x_tr_sl=auto&_x_tr_tl=pt&_x_tr_hl=en&_x_tr_pto=wapp Português]''' | '''[https://wiki-iucnapesportal-org.translate.goog/index.php/Bakossi_National_Park?_x_tr_sl=auto&_x_tr_tl=es&_x_tr_hl=en&_x_tr_pto=wapp Español]''' | '''[https://wiki-iucnapesportal-org.translate.goog/index.php/Bakossi_National_Park?_x_tr_sl=auto&_x_tr_tl=id&_x_tr_hl=en&_x_tr_pto=wapp Bahasa Indonesia]''' | '''[https://wiki-iucnapesportal-org.translate.goog/index.php/Bakossi_National_Park?_x_tr_sl=auto&_x_tr_tl=ms&_x_tr_hl=en&_x_tr_pto=wapp Melayu]''' |
| − | <div style="float: right"> | + | |
| − | {{#display_map: height= | + | __TOC__ |
| − | |5.069109, 9.586158~[[Bakossi National Park]]~ | + | = Summary = |
| − | }} | + | |
| − | </div> | + | <div style="float: right">{{#display_map: height=190px | width=300px | scrollzoom=off | zoom=5 | layers= OpenStreetMap, OpenTopoMap|5.069109, 9.586158~[[Bakossi National Park]]~'Pan troglodytes ellioti''}}</div> |
* Nigeria-Cameroon chimpanzees (''Pan troglodytes ellioti'') are present in Bakossi National Park. | * Nigeria-Cameroon chimpanzees (''Pan troglodytes ellioti'') are present in Bakossi National Park. | ||
* The population size is unknown. | * The population size is unknown. | ||
| Line 21: | Line 13: | ||
* Chimpanzees are mainly threatened by hunting. | * Chimpanzees are mainly threatened by hunting. | ||
* Conservation activities are not documented. | * Conservation activities are not documented. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Bakossi National Park is located in western Cameroon, to the south of the | + | |
| − | The site is a hotspot for many primate species, including the drill (''Mandrillus leucophaeus''), one of the most endangered primate species in the world, and the chimpanzee (''Pan troglodytes''). Other primates include | + | = Site characteristics = |
| − | The Bakossi forests support several small streams, cascading waterfalls and deep pools, and the Mungo River which flows through the park. Along the way, thousands of people far beyond the site depend on the river for their livelihoods through activities such as fishing, sand extraction, and logs and food transportation ( | + | |
| + | Bakossi National Park is located in western Cameroon, to the south of the Banyang-Mbo Wildlife Sanctuary and covers an area of 29,320 ha. The park was created in 2008 to protect its rich plant diversity. The altitude in the park ranges from 300 m to 1,895 m above sea level, giving rise to three main vegetation types: sub-montane forest, Atlantic forest of the North West type with semi-deciduous elements, and the Atlantic Biafran forest rich in ''Caesalpiniaceae''. This accounts for the huge floral variety of the area and a high level of endemism, and a corresponding high diversity of fauna species (Morgan et al. 2011, Kupsch et al. 2024). The site is a hotspot for many primate species, including the drill (''Mandrillus leucophaeus''), one of the most endangered primate species in the world, and the Nigeria-Cameroon chimpanzee (''Pan troglodytes ellioti''). Other primates include red-eared guenon, Preuss’s guenon, crowned monkey, putty-nosed monkey, mona monkey and other important mammals like red river hog, yellow-backed duiker, Bay duiker, Ogilby duiker, blue duiker, and tree pangolin (Boekee et al. 2021, Kupsch et al. 2024). The Bakossi forests support several small streams, cascading waterfalls and deep pools, and the Mungo River which flows through the park. Along the way, thousands of people far beyond the site depend on the river for their livelihoods through activities such as fishing, sand extraction, and logs and food transportation (WWF). | ||
'''Table 1. Basic site information for Bakossi National Park''' | '''Table 1. Basic site information for Bakossi National Park''' | ||
| − | {| border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" class=" | + | {| border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" class="Site_characteristics-table" |
| − | | Area | + | |Species |
| + | |'Pan troglodytes ellioti'' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Area | ||
|293 km² | |293 km² | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Coordinates | |Coordinates | ||
| − | |5.069109, 9.586158 | + | |Lat: 5.069109 , Lon: 9.586158 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Type of site |
| − | |National Park | + | |Protected area (National Park) |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |Habitat types | + | |Habitat types |
| − | |Subtropical/tropical moist lowland forest, | + | |Subtropical/tropical moist lowland forest, Subtropical/tropical moist montane forest |
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Type of governance | ||
| + | | | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | = Ape status = | + | [https://www.iucnredlist.org/resources/habitat-classification-scheme IUCN habitat categories] [[Site designations]] |
| + | |||
| + | = Ape status = | ||
| − | In a survey of the southeastern section of the park, chimpanzees were recorded entirely in the montane forest ( | + | In a survey of the southeastern section of the park, chimpanzees were recorded entirely in the montane forest (Mbua 2021). However, chimpanzees have also been found in relatively large numbers in the southern and western parts of the park, which are also characterized by lower altitude ranges (Kupsch et al. 2024). Due to lacking data from past years, there are no trends on the population or abundance of chimpanzees available. However, in 2023, the relative abundance of chimpanzees in Bakossi NP was high compared to other important protected areas with chimpanzee presence in the Southwest Region of Cameroon (Mt. Cameroon and Korup NP, Banyang Mbo Wildlife Sanctuary; Kupsch et al. 2024). |
| − | '''Table 2. Ape population estimates | + | '''Table 2. Ape population estimates reported for Bakossi National Park''' |
| − | {| border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" class=" | + | {| border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" class="Ape_status-table" |
| − | ! Species | + | !Species |
| − | ! Year | + | !Year |
| − | ! | + | !Occurrence |
| − | ! Density estimate [ind./ km²] (95% CI) | + | !Encounter or vistation rate (nests/km; ind/day) |
| − | ! | + | !Density estimate [ind./ km²] (95% CI) |
| − | ! | + | !Abundance estimate (95% CI) |
| − | ! | + | !Survey area |
| − | ! Source | + | !Sampling method |
| − | ! Comments | + | !Analytical framework |
| − | ! A.P.E.S. database ID | + | !Source |
| + | !Comments | ||
| + | !A.P.E.S. database ID | ||
|- | |- | ||
|''Pan troglodytes ellioti'' | |''Pan troglodytes ellioti'' | ||
| − | | | + | |2021.0 |
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | |||
|Southeast of Bakossi National Park, approx. 12 km2 | |Southeast of Bakossi National Park, approx. 12 km2 | ||
| − | | | + | |Reconnaissance walk |
| − | | | + | | |
| − | |Reconnaissance walk covered a total of 61 km. Signs recorded: | + | |Mbua 2021 |
| + | |Reconnaissance walk covered a total of 61 km. Signs recorded: nest clusters 0.07 per km, and feeding signs 0.03 per km | ||
| | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |''Pan troglodytes ellioti'' |
| + | |2021.0 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| + | |Bakossi National Park | ||
| + | |Reconnaissance walk | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |Calculated based on data from Boekee et al. 2021 | ||
| + | |Survey effort 70 km. 0.2 nest cluster enc/km | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |''Pan troglodytes ellioti'' |
| + | |2021.0 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| + | |Bakossi National Park | ||
| + | |Camera trap | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |Calculated based on data from Boekee et al. 2021 | ||
| + | |Survey effort 545 camera days; 0.18 camera rec/100d +/- 0.18 (SE) | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |''Pan troglodytes ellioti'' |
| + | |2023.0 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| + | |Bakossi National Park | ||
| + | |Reconnaissance walk | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |Kupsch et al. 2024 | ||
| + | |Survey effort 175.7 km. 0.33 nest cluster enc/km +/- 0.08 (SE) | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |''Pan troglodytes ellioti'' |
| − | | | + | |2023.0 |
| − | | | + | | |
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |Bakossi National Park | ||
| + | |Camera trap | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |Kupsch et al. 2024 | ||
| + | |Survey effort 1,131 camera days. 0.97 camera rec/100d +/- 0.71 (SE) | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | |} |
| − | | | + | |
| + | |||
| + | = Threats = | ||
| + | |||
| + | Hunting is a major threat to large mammals, including chimpanzees, in Bakossi National Park (Kupsch et al. 2024). | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Table 3. Threats to apes reported for Bakossi National Park''' | ||
| + | {| border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" class="Threats-table" | ||
| + | !Category | ||
| + | !Specific threats | ||
| + | !Threat level | ||
| + | !Description | ||
| + | !Year of threat | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |10 Geological events |
| − | | | + | | |
| − | | | + | |Absent |
| + | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |12 Other threat |
| + | | | ||
| + | |Absent | ||
| | | | ||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |5 Biological resource use | ||
| + | |5.1 Hunting & collecting terrestrial animals | ||
| + | |High (more than 70% of population affected) | ||
| + | |Hunting of large mammals (BirdLife International 2023). Cartridge shell rate 0.32 enc/h ± 0.09 (SE) and trap rate 0.32 enc/h ± 0.11 (SE) from recces in 2023 (Kupsch et al. 2024); gunshot rate 14.03 rec/100d ± 5.48 from acoustic sensors in 2023 (Kupsch et al. 2024). | ||
| + | |Ongoing (2024) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |1 Residential & commercial development | ||
| + | |1.1 Residential areas | ||
| + | |Present (unknown severity) | ||
| + | |There are settlements inside the park (southern sector) which are officially illegal and linked to farms in the site (Boekee et al. 2021, Kupsch et al. 2024). | ||
| + | |2021-Ongoing (2024) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |2 Agriculture & aquaculture | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |Present (unknown severity) | ||
| + | |Agricultural encroachment from villages situated inside and outside the park (Boekee et al. 2021). | ||
| + | |2021-Ongoing (2024) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |4 Transportation & service corridors | ||
| + | |4.1 Roads & railroads | ||
| + | |Present (unknown severity) | ||
| + | |An old, abandoned road along the south-eastern edge of Bakossi is being reopened with European funds (BirdLife International 2023). | ||
| + | |Ongoing (2023) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |6 Human intrusions & disturbance | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |Present (unknown severity) | ||
| + | |Military-political crisis in the entire region with ranging rebel groups in and around Bakossi National Park. Since 2021, the park has been accessible from the east again for research and eco guards (Boekee et al. 2021, Mbua 2021); since 2023, the entire park is accessible again (Kupsch et al. 2024). | ||
| + | |2018-2021 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |3 Energy production & mining |
| | | | ||
|Unknown | |Unknown | ||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |7 Natural system modifications |
| | | | ||
|Unknown | |Unknown | ||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |8 Invasive & other problematic species, genes & diseases |
| | | | ||
|Unknown | |Unknown | ||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |9 Pollution |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 11 | + | |11 Climate change & severe weather |
| | | | ||
|Unknown | |Unknown | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://www.iucnredlist.org/resources/threat-classification-scheme IUCN Threats list] | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Conservation activities = | ||
| + | |||
| + | Bakossi National Park is under the administration of the Cameroonian Ministry of Forestry and Wildlife (MINFOF), which is supported by the PSMNR-SWR development program and follows a collaborative management approach (PSMNR-SWR n.d.). In addition to support for infrastructure, households, education and training, this also includes protection activities such as demarcation and patrolling, as well as bio-monitoring (Kupsch et al. 2024). In addition to communities and their members, community-based organizations are also involved in management. Bakossi National Park has been included in the PSMNR-SWR development scheme in 2018. Before it was part of the WWF coastal forests programme (WWF), however, little is documented on the conservation activities from that time. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Table 4. Conservation activities reported for Bakossi National Park''' | ||
| + | {| border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" class="Conservation_activities-table" | ||
| + | !Category | ||
| + | !Specific activity | ||
| + | !Description | ||
| + | !Implementing organization(s) | ||
| + | !Year of activity | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |2 Counter-wildlife crime | ||
| + | |2.3 Conduct regular anti-poaching patrols | ||
| + | |Anti-poaching patrols evaluation and design (PSMNR-SWR n.d., BNP n.d.). | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |2018-Ongoing (2024) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |4 Education & awareness |
| + | |4.2 Involve local community in ape research and conservation management | ||
| + | |Involvement in bio-monitoring as part of a collaborative management approach (Kupsch et al. 2024). | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | |2023-Ongoing (2024) |
| + | |- | ||
| + | |5 Protection & restoration | ||
| + | |5.2 Legally protect ape habitat | ||
| + | |The park was established in 2008. | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |2008-Ongoing (2024) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |5 Protection & restoration | ||
| + | |5.5 Demarcate and enforce boundaries of protected areas | ||
| + | |Boundary demarcation activities of park staff and communities (PSMNR-SWR n.d.). | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |2008-Ongoing (2024) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |7 Economic & other incentives | ||
| + | |7.2 Provide non-monetary benefits to local communities for sustainably managing their forest and its wildlife (e.g., better education, infrastructure development) | ||
| + | |Farming equipment, scholarships, community infrastructure development, small scale piggery and non-timber products value chain improvement (PSMNR-SWR n.d., BNP n.d.). | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |2018-Ongoing (2024) | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Conservation activities list (Junker et al. 2017)]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Challenges = | ||
| + | |||
| + | Since 2017, there has been a military-political crisis with a very poor security situation in the Anglophone regions of Cameroon, which has made law enforcement impossible. Eco-guards and researchers could not enter the national park and most of the villages within and adjacent to it (Boekee et al. 2021, Kupsch et al. 2024). Since 2021, the park has been accessible to eco-guards and researchers in its eastern and central sections (Boekee et al. 2021). The entire park area has been accessible again since 2023, subject to due caution and arrival from the south, east or north. (Kupsch et al. 2024). | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Table 5. Challenges reported for Bakossi National Park''' | ||
| + | {| border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" class="Challenges-table" | ||
| + | !Challenges | ||
| + | !Specific challenges | ||
| + | !Source | ||
| + | !Year(s) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| + | |2 Resources and capacity | ||
| + | |2.6 Lack of biomonitoring/survey data | ||
| + | |Boekee et al. 2021, Kupsch et al. 2024 | ||
| + | |Ongoing (2024) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |4 Institutional support | ||
| + | |4.1 Lack of law enforcement | ||
| + | |Boekee et al. 2021, Kupsch et al. 2024 | ||
| + | |Ongoing (2024) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |6 Safety and stability | ||
| + | |6.1 Political/economic instabilty | ||
| + | |Boekee et al. 2021, Kupsch et al. 2024 | ||
| + | |Ongoing (2024) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |6 Safety and stability | ||
| + | |6.2 Insecurity | ||
| + | |Boekee et al. 2021, Kupsch et al. 2024 | ||
| + | |Ongoing (2024) | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | '''Table | + | = Enablers = |
| − | {| border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" class=" | + | |
| − | ! | + | |
| − | !Specific | + | |
| − | ! | + | '''Table 6. Enablers reported for Bakossi National Park''' |
| − | !Year | + | {| border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" class="enabler-table" |
| + | !Enablers | ||
| + | !Specific enablers | ||
| + | !Source | ||
| + | !Year(s) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |1 | + | |1 Site management |
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |2 Resources and capacity |
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |3 Engaged community |
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |4 Institutional support |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |5 Ecological context |
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |6 Safety and stability |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | = Research activities = | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | The landscapes in and around Bakossi National Park are very heterogeneous and are home to a rich diversity of avifauna and flora, on which research has so far focused largely (BirdLife International 2023). Research objects, surveys or data on large mammals and especially chimpanzees are scarce, incomplete or lost (Kupsch et al. 2024). Since the military-political crisis in the region subsided, initial attempts have been made to assess the status of chimpanzees in Bakossi National Park, including area-wide recce, acoustic and camera surveys and a community-based monitoring in hotspot areas of the park (Kupsch et al. 2024). The results of the surveys and reports are expected in 2025. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | = Documented behaviours = | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | '''Table | + | '''Table 7. Behaviours documented for Bakossi National Park''' |
| − | {| border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" class=" | + | {| border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" class="behaviours-table" |
| − | ! | + | !Behavior |
!Source | !Source | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Not reported | |Not reported | ||
| | | | ||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
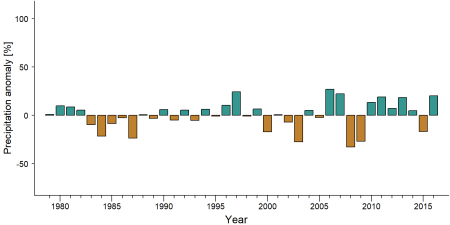
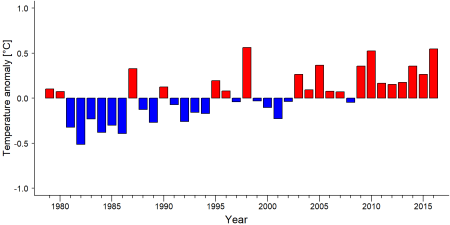
= Exposure to climate change impacts = | = Exposure to climate change impacts = | ||
As part of a study on the exposure of African great ape sites to climate change impacts, Kiribou et al. (2024) extracted climate data and data on projected extreme climate impact events for the site. Climatological characteristics were derived from observation-based climate data provided by the Inter-Sectoral Impact Model Intercomparison Project (ISIMIP, www.isimip.org). Parameters were calculated as the average across each 30-year period. For 1981-2010, the EWEMBI dataset from ISIMIP2a was used. For the two future periods (2021-2050 and 2071-2099) ISIMIP2b climate data based on four CMIP5 global climate models were used. For future projections, two Representative Concentration Pathways (RCP) were used. RCP 2.6 is a scenario with strong mitigation measures in which global temperatures would likely rise below 2°C. RCP 6.0 is a scenario with medium emissions in which global temperatures would likely rise up to 3°C by 2100. For the number of days with heavy precipitation events, the 98th percentile of all precipitation days (>1mm/d) was calculated for the 1979-2013 reference period as a threshold for a heavy precipitation event. Then, for each year, the number of days above that threshold was derived. The figures on temperature and precipitation anomaly show the deviation from the mean temperature and mean precipitation for the 1979-2013 reference period. | As part of a study on the exposure of African great ape sites to climate change impacts, Kiribou et al. (2024) extracted climate data and data on projected extreme climate impact events for the site. Climatological characteristics were derived from observation-based climate data provided by the Inter-Sectoral Impact Model Intercomparison Project (ISIMIP, www.isimip.org). Parameters were calculated as the average across each 30-year period. For 1981-2010, the EWEMBI dataset from ISIMIP2a was used. For the two future periods (2021-2050 and 2071-2099) ISIMIP2b climate data based on four CMIP5 global climate models were used. For future projections, two Representative Concentration Pathways (RCP) were used. RCP 2.6 is a scenario with strong mitigation measures in which global temperatures would likely rise below 2°C. RCP 6.0 is a scenario with medium emissions in which global temperatures would likely rise up to 3°C by 2100. For the number of days with heavy precipitation events, the 98th percentile of all precipitation days (>1mm/d) was calculated for the 1979-2013 reference period as a threshold for a heavy precipitation event. Then, for each year, the number of days above that threshold was derived. The figures on temperature and precipitation anomaly show the deviation from the mean temperature and mean precipitation for the 1979-2013 reference period. | ||
| + | |||
The estimated exposure to future extreme climate impact events (crop failure, drought, river flood, wildfire, tropical cyclone, and heatwave) is based on a published dataset by Lange et al. 2020 derived from ISIMIP2b data. The same global climate models and RCPs as described above were used. Within each 30-year period, the number of years with an extreme event and the average proportion of the site affected were calculated (Kiribou et al. 2024). | The estimated exposure to future extreme climate impact events (crop failure, drought, river flood, wildfire, tropical cyclone, and heatwave) is based on a published dataset by Lange et al. 2020 derived from ISIMIP2b data. The same global climate models and RCPs as described above were used. Within each 30-year period, the number of years with an extreme event and the average proportion of the site affected were calculated (Kiribou et al. 2024). | ||
| − | '''Table | + | '''Table 8. Estimated past and projected climatological characteristics in Bakossi National Park''' |
| − | {| border= | + | {| border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" class="clima-table" |
| − | + | !'''Value''' | |
| − | + | !'''1981-2010''' | |
| − | + | !'''2021-2050, RCP 2.6''' | |
| − | + | !'''2021-2050, RCP 6.0''' | |
| − | + | !'''2071-2099, RCP 2.6''' | |
| − | + | !'''2071-2099, RCP 6.0''' | |
|- | |- | ||
|Mean temperature [°C] | |Mean temperature [°C] | ||
| Line 316: | Line 398: | ||
|9 | |9 | ||
|8.9 | |8.9 | ||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
| − | '''Table | + | '''Table 9. Projected exposure of apes to extreme climate impact events in Bakossi National Park''' |
| − | {| border= | + | {| border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" class="clima2-table" |
| − | + | !'''Type''' | |
| − | + | !'''No. of years with event (2021-2050, RCP 2.6)''' | |
| − | + | !'''% of site exposed (2021-2050, RCP 2.6)''' | |
| − | + | !'''No. of years with event (2021-2050, RCP 6.0)''' | |
| − | + | !'''% of site exposed (2021-2050, RCP 6.0)''' | |
| − | + | !'''No. of years with event (2070-2099, RCP 2.6)''' | |
| − | + | !'''% of site exposed (2070-2099, RCP 2.6)''' | |
| − | + | !'''No. of years with event (2070-2099, RCP 6.0)''' | |
| − | + | !'''% of site exposed (2070-2099, RCP 6.0)''' | |
|- | |- | ||
|Crop failure | |Crop failure | ||
| Line 391: | Line 472: | ||
|29 | |29 | ||
|0.66 | |0.66 | ||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | =External links= | + | <div><ul><li style="display: inline-block; vertical-align: top;"> [[File: PrecipAnomaly_Bakossi NP.png | 450px | thumb| right | Precipitation anomaly in Bakossi National Park]] </li><li style="display: inline-block; vertical-align: top;"> [[File: TempAnomaly_Bakossi NP.png | 450px | thumb| right | Temperature anomaly in Bakossi National Park]] </li></ul></div> |
| + | |||
| + | = External links = | ||
| + | |||
[https://cameroon.panda.org/places_landscapes/coastal_forests_programme/bakossi_national_park/ WWF Bakossi NP] | [https://cameroon.panda.org/places_landscapes/coastal_forests_programme/bakossi_national_park/ WWF Bakossi NP] | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Relevant datasets = | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
= References = | = References = | ||
| − | + | ||
BirdLife International (2023) Important Bird Areas factsheet: Bakossi mountains. Downloaded from http://www.birdlife.org on 15/05/2023.<br> | BirdLife International (2023) Important Bird Areas factsheet: Bakossi mountains. Downloaded from http://www.birdlife.org on 15/05/2023.<br> | ||
| − | Kiribou, R., Tehoda, P., Chukwu, O., Bempah, G., Kühl, H. S., Ferreira, J., ... & Heinicke, S. (2024). Exposure of African ape sites to climate change impacts. PLOS Climate, 3(2), e0000345.<br> | + | BNP (n.d.). About Bakossi National Park. https://bakossinationalpark.org/about-the-park/ <br> |
| − | <br> | + | Boekee, K., Motale, T., and Arong, C. (2021). Bakossi National Park - Reconnaissance survey report. Explorative survey in preparation to establish bio-monitoring surveys. Project report. PSMNR-SWR, Buea. 24p. <br> |
| − | '''Page | + | Kiribou, R., Tehoda, P., Chukwu, O., Bempah, G., Kühl, H. S., Ferreira, J., ... & Heinicke, S. (2024). Exposure of African ape sites to climate change impacts. PLOS Climate, 3(2), e0000345. <br> |
| + | Mbua A. A. (2021). Habitat conditions in relation to the distribution of chimpanzees in the South East Cluster of Bakossi National Park South West Region of Cameroon. End of internship report. Submitted to obtain a B.Sc. degree. Advance School of Engineering of Maroua, Cameroon. 73p. <br> | ||
| + | Morgan, B. J., Adeleke, A., Bassey, T., Bergl, R., Dunn, A., Fotso, R., et al. (2011). Regional action plan for the conservation of the Nigeria–Cameroon chimpanzee (Pan troglodytes ellioti). IUCN/SSC Primate Specialist Group and Zoological Society of San Diego. <br> | ||
| + | Kupsch, D., Motale, T., and Sumbede, A. (2024). Status of large mammals and human activities in Bakossi National Park. PSMNR-SWR bio-monitoring report. Buea, Cameroon. 32p. <br> | ||
| + | PSMNR-SWR (n.d.). About PSMNR-SWR. https://psmnrswr.org/about-psmnr-swr/ <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''Page created by: '''Denish Kupsch & Anthoine Sumbede''' Date:''' 2023-05-13 | ||
Latest revision as of 09:13, 18 March 2025
Central Africa > Cameroon > Bakossi National Park
Français | Português | Español | Bahasa Indonesia | Melayu
Summary
- Nigeria-Cameroon chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes ellioti) are present in Bakossi National Park.
- The population size is unknown.
- The chimpanzee population trend is unknown.
- The site has a total size of 293km².
- Chimpanzees are mainly threatened by hunting.
- Conservation activities are not documented.
Site characteristics
Bakossi National Park is located in western Cameroon, to the south of the Banyang-Mbo Wildlife Sanctuary and covers an area of 29,320 ha. The park was created in 2008 to protect its rich plant diversity. The altitude in the park ranges from 300 m to 1,895 m above sea level, giving rise to three main vegetation types: sub-montane forest, Atlantic forest of the North West type with semi-deciduous elements, and the Atlantic Biafran forest rich in Caesalpiniaceae. This accounts for the huge floral variety of the area and a high level of endemism, and a corresponding high diversity of fauna species (Morgan et al. 2011, Kupsch et al. 2024). The site is a hotspot for many primate species, including the drill (Mandrillus leucophaeus), one of the most endangered primate species in the world, and the Nigeria-Cameroon chimpanzee (Pan troglodytes ellioti). Other primates include red-eared guenon, Preuss’s guenon, crowned monkey, putty-nosed monkey, mona monkey and other important mammals like red river hog, yellow-backed duiker, Bay duiker, Ogilby duiker, blue duiker, and tree pangolin (Boekee et al. 2021, Kupsch et al. 2024). The Bakossi forests support several small streams, cascading waterfalls and deep pools, and the Mungo River which flows through the park. Along the way, thousands of people far beyond the site depend on the river for their livelihoods through activities such as fishing, sand extraction, and logs and food transportation (WWF).
Table 1. Basic site information for Bakossi National Park
| Species | 'Pan troglodytes ellioti |
| Area | 293 km² |
| Coordinates | Lat: 5.069109 , Lon: 9.586158 |
| Type of site | Protected area (National Park) |
| Habitat types | Subtropical/tropical moist lowland forest, Subtropical/tropical moist montane forest |
| Type of governance |
IUCN habitat categories Site designations
Ape status
In a survey of the southeastern section of the park, chimpanzees were recorded entirely in the montane forest (Mbua 2021). However, chimpanzees have also been found in relatively large numbers in the southern and western parts of the park, which are also characterized by lower altitude ranges (Kupsch et al. 2024). Due to lacking data from past years, there are no trends on the population or abundance of chimpanzees available. However, in 2023, the relative abundance of chimpanzees in Bakossi NP was high compared to other important protected areas with chimpanzee presence in the Southwest Region of Cameroon (Mt. Cameroon and Korup NP, Banyang Mbo Wildlife Sanctuary; Kupsch et al. 2024).
Table 2. Ape population estimates reported for Bakossi National Park
| Species | Year | Occurrence | Encounter or vistation rate (nests/km; ind/day) | Density estimate [ind./ km²] (95% CI) | Abundance estimate (95% CI) | Survey area | Sampling method | Analytical framework | Source | Comments | A.P.E.S. database ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pan troglodytes ellioti | 2021.0 | Southeast of Bakossi National Park, approx. 12 km2 | Reconnaissance walk | Mbua 2021 | Reconnaissance walk covered a total of 61 km. Signs recorded: nest clusters 0.07 per km, and feeding signs 0.03 per km | ||||||
| Pan troglodytes ellioti | 2021.0 | Bakossi National Park | Reconnaissance walk | Calculated based on data from Boekee et al. 2021 | Survey effort 70 km. 0.2 nest cluster enc/km | ||||||
| Pan troglodytes ellioti | 2021.0 | Bakossi National Park | Camera trap | Calculated based on data from Boekee et al. 2021 | Survey effort 545 camera days; 0.18 camera rec/100d +/- 0.18 (SE) | ||||||
| Pan troglodytes ellioti | 2023.0 | Bakossi National Park | Reconnaissance walk | Kupsch et al. 2024 | Survey effort 175.7 km. 0.33 nest cluster enc/km +/- 0.08 (SE) | ||||||
| Pan troglodytes ellioti | 2023.0 | Bakossi National Park | Camera trap | Kupsch et al. 2024 | Survey effort 1,131 camera days. 0.97 camera rec/100d +/- 0.71 (SE) |
Threats
Hunting is a major threat to large mammals, including chimpanzees, in Bakossi National Park (Kupsch et al. 2024).
Table 3. Threats to apes reported for Bakossi National Park
| Category | Specific threats | Threat level | Description | Year of threat |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 Geological events | Absent | |||
| 12 Other threat | Absent | |||
| 5 Biological resource use | 5.1 Hunting & collecting terrestrial animals | High (more than 70% of population affected) | Hunting of large mammals (BirdLife International 2023). Cartridge shell rate 0.32 enc/h ± 0.09 (SE) and trap rate 0.32 enc/h ± 0.11 (SE) from recces in 2023 (Kupsch et al. 2024); gunshot rate 14.03 rec/100d ± 5.48 from acoustic sensors in 2023 (Kupsch et al. 2024). | Ongoing (2024) |
| 1 Residential & commercial development | 1.1 Residential areas | Present (unknown severity) | There are settlements inside the park (southern sector) which are officially illegal and linked to farms in the site (Boekee et al. 2021, Kupsch et al. 2024). | 2021-Ongoing (2024) |
| 2 Agriculture & aquaculture | Present (unknown severity) | Agricultural encroachment from villages situated inside and outside the park (Boekee et al. 2021). | 2021-Ongoing (2024) | |
| 4 Transportation & service corridors | 4.1 Roads & railroads | Present (unknown severity) | An old, abandoned road along the south-eastern edge of Bakossi is being reopened with European funds (BirdLife International 2023). | Ongoing (2023) |
| 6 Human intrusions & disturbance | Present (unknown severity) | Military-political crisis in the entire region with ranging rebel groups in and around Bakossi National Park. Since 2021, the park has been accessible from the east again for research and eco guards (Boekee et al. 2021, Mbua 2021); since 2023, the entire park is accessible again (Kupsch et al. 2024). | 2018-2021 | |
| 3 Energy production & mining | Unknown | |||
| 7 Natural system modifications | Unknown | |||
| 8 Invasive & other problematic species, genes & diseases | Unknown | |||
| 9 Pollution | Unknown | |||
| 11 Climate change & severe weather | Unknown |
Conservation activities
Bakossi National Park is under the administration of the Cameroonian Ministry of Forestry and Wildlife (MINFOF), which is supported by the PSMNR-SWR development program and follows a collaborative management approach (PSMNR-SWR n.d.). In addition to support for infrastructure, households, education and training, this also includes protection activities such as demarcation and patrolling, as well as bio-monitoring (Kupsch et al. 2024). In addition to communities and their members, community-based organizations are also involved in management. Bakossi National Park has been included in the PSMNR-SWR development scheme in 2018. Before it was part of the WWF coastal forests programme (WWF), however, little is documented on the conservation activities from that time.
Table 4. Conservation activities reported for Bakossi National Park
| Category | Specific activity | Description | Implementing organization(s) | Year of activity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 Counter-wildlife crime | 2.3 Conduct regular anti-poaching patrols | Anti-poaching patrols evaluation and design (PSMNR-SWR n.d., BNP n.d.). | 2018-Ongoing (2024) | |
| 4 Education & awareness | 4.2 Involve local community in ape research and conservation management | Involvement in bio-monitoring as part of a collaborative management approach (Kupsch et al. 2024). | 2023-Ongoing (2024) | |
| 5 Protection & restoration | 5.2 Legally protect ape habitat | The park was established in 2008. | 2008-Ongoing (2024) | |
| 5 Protection & restoration | 5.5 Demarcate and enforce boundaries of protected areas | Boundary demarcation activities of park staff and communities (PSMNR-SWR n.d.). | 2008-Ongoing (2024) | |
| 7 Economic & other incentives | 7.2 Provide non-monetary benefits to local communities for sustainably managing their forest and its wildlife (e.g., better education, infrastructure development) | Farming equipment, scholarships, community infrastructure development, small scale piggery and non-timber products value chain improvement (PSMNR-SWR n.d., BNP n.d.). | 2018-Ongoing (2024) |
Conservation activities list (Junker et al. 2017)
Challenges
Since 2017, there has been a military-political crisis with a very poor security situation in the Anglophone regions of Cameroon, which has made law enforcement impossible. Eco-guards and researchers could not enter the national park and most of the villages within and adjacent to it (Boekee et al. 2021, Kupsch et al. 2024). Since 2021, the park has been accessible to eco-guards and researchers in its eastern and central sections (Boekee et al. 2021). The entire park area has been accessible again since 2023, subject to due caution and arrival from the south, east or north. (Kupsch et al. 2024).
Table 5. Challenges reported for Bakossi National Park
| Challenges | Specific challenges | Source | Year(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 Resources and capacity | 2.6 Lack of biomonitoring/survey data | Boekee et al. 2021, Kupsch et al. 2024 | Ongoing (2024) |
| 4 Institutional support | 4.1 Lack of law enforcement | Boekee et al. 2021, Kupsch et al. 2024 | Ongoing (2024) |
| 6 Safety and stability | 6.1 Political/economic instabilty | Boekee et al. 2021, Kupsch et al. 2024 | Ongoing (2024) |
| 6 Safety and stability | 6.2 Insecurity | Boekee et al. 2021, Kupsch et al. 2024 | Ongoing (2024) |
Enablers
Table 6. Enablers reported for Bakossi National Park
| Enablers | Specific enablers | Source | Year(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Site management | |||
| 2 Resources and capacity | |||
| 3 Engaged community | |||
| 4 Institutional support | |||
| 5 Ecological context | |||
| 6 Safety and stability |
Research activities
The landscapes in and around Bakossi National Park are very heterogeneous and are home to a rich diversity of avifauna and flora, on which research has so far focused largely (BirdLife International 2023). Research objects, surveys or data on large mammals and especially chimpanzees are scarce, incomplete or lost (Kupsch et al. 2024). Since the military-political crisis in the region subsided, initial attempts have been made to assess the status of chimpanzees in Bakossi National Park, including area-wide recce, acoustic and camera surveys and a community-based monitoring in hotspot areas of the park (Kupsch et al. 2024). The results of the surveys and reports are expected in 2025.
Documented behaviours
Table 7. Behaviours documented for Bakossi National Park
| Behavior | Source |
|---|---|
| Not reported |
Exposure to climate change impacts
As part of a study on the exposure of African great ape sites to climate change impacts, Kiribou et al. (2024) extracted climate data and data on projected extreme climate impact events for the site. Climatological characteristics were derived from observation-based climate data provided by the Inter-Sectoral Impact Model Intercomparison Project (ISIMIP, www.isimip.org). Parameters were calculated as the average across each 30-year period. For 1981-2010, the EWEMBI dataset from ISIMIP2a was used. For the two future periods (2021-2050 and 2071-2099) ISIMIP2b climate data based on four CMIP5 global climate models were used. For future projections, two Representative Concentration Pathways (RCP) were used. RCP 2.6 is a scenario with strong mitigation measures in which global temperatures would likely rise below 2°C. RCP 6.0 is a scenario with medium emissions in which global temperatures would likely rise up to 3°C by 2100. For the number of days with heavy precipitation events, the 98th percentile of all precipitation days (>1mm/d) was calculated for the 1979-2013 reference period as a threshold for a heavy precipitation event. Then, for each year, the number of days above that threshold was derived. The figures on temperature and precipitation anomaly show the deviation from the mean temperature and mean precipitation for the 1979-2013 reference period.
The estimated exposure to future extreme climate impact events (crop failure, drought, river flood, wildfire, tropical cyclone, and heatwave) is based on a published dataset by Lange et al. 2020 derived from ISIMIP2b data. The same global climate models and RCPs as described above were used. Within each 30-year period, the number of years with an extreme event and the average proportion of the site affected were calculated (Kiribou et al. 2024).
Table 8. Estimated past and projected climatological characteristics in Bakossi National Park
| Value | 1981-2010 | 2021-2050, RCP 2.6 | 2021-2050, RCP 6.0 | 2071-2099, RCP 2.6 | 2071-2099, RCP 6.0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean temperature [°C] | 25.3 | 26.4 | 26.3 | 26.6 | 27.6 |
| Annual precipitation [mm] | 2566 | 2672 | 2686 | 2749 | 2756 |
| Max no. consecutive dry days (per year) | 36.5 | 29.3 | 34.4 | 32.6 | 36 |
| No. days with heavy precipitation (per year) | 6 | 8.2 | 8 | 9 | 8.9 |
Table 9. Projected exposure of apes to extreme climate impact events in Bakossi National Park
| Type | No. of years with event (2021-2050, RCP 2.6) | % of site exposed (2021-2050, RCP 2.6) | No. of years with event (2021-2050, RCP 6.0) | % of site exposed (2021-2050, RCP 6.0) | No. of years with event (2070-2099, RCP 2.6) | % of site exposed (2070-2099, RCP 2.6) | No. of years with event (2070-2099, RCP 6.0) | % of site exposed (2070-2099, RCP 6.0) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crop failure | 3.5 | 0.33 | 4 | 0 | 0.5 | 0.13 | 5.5 | 0.01 |
| Drought | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Heatwave | 8 | 100 | 7 | 100 | 7.5 | 100 | 10.5 | 100 |
| River flood | 2.5 | 0.7 | 1 | 0.86 | 1.5 | 2.05 | 5 | 1.81 |
| Tropical cyclone | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Wildfire | 30 | 0.63 | 30 | 0.65 | 29 | 0.63 | 29 | 0.66 |
External links
Relevant datasets
References
BirdLife International (2023) Important Bird Areas factsheet: Bakossi mountains. Downloaded from http://www.birdlife.org on 15/05/2023.
BNP (n.d.). About Bakossi National Park. https://bakossinationalpark.org/about-the-park/
Boekee, K., Motale, T., and Arong, C. (2021). Bakossi National Park - Reconnaissance survey report. Explorative survey in preparation to establish bio-monitoring surveys. Project report. PSMNR-SWR, Buea. 24p.
Kiribou, R., Tehoda, P., Chukwu, O., Bempah, G., Kühl, H. S., Ferreira, J., ... & Heinicke, S. (2024). Exposure of African ape sites to climate change impacts. PLOS Climate, 3(2), e0000345.
Mbua A. A. (2021). Habitat conditions in relation to the distribution of chimpanzees in the South East Cluster of Bakossi National Park South West Region of Cameroon. End of internship report. Submitted to obtain a B.Sc. degree. Advance School of Engineering of Maroua, Cameroon. 73p.
Morgan, B. J., Adeleke, A., Bassey, T., Bergl, R., Dunn, A., Fotso, R., et al. (2011). Regional action plan for the conservation of the Nigeria–Cameroon chimpanzee (Pan troglodytes ellioti). IUCN/SSC Primate Specialist Group and Zoological Society of San Diego.
Kupsch, D., Motale, T., and Sumbede, A. (2024). Status of large mammals and human activities in Bakossi National Park. PSMNR-SWR bio-monitoring report. Buea, Cameroon. 32p.
PSMNR-SWR (n.d.). About PSMNR-SWR. https://psmnrswr.org/about-psmnr-swr/
Page created by: Denish Kupsch & Anthoine Sumbede Date: 2023-05-13