Difference between revisions of "Zone Humide d'Ebogo"
| (5 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Central Africa]] > [[Cameroon]] > [[Zone Humide d'Ebogo]] | [[Central Africa]] > [[Cameroon]] > [[Zone Humide d'Ebogo]] | ||
| − | = | + | '''[https://wiki-iucnapesportal-org.translate.goog/index.php/Zone_Humide_d'Ebogo?_x_tr_sl=auto&_x_tr_tl=fr&_x_tr_hl=en&_x_tr_pto=wapp Français]''' | '''[https://wiki-iucnapesportal-org.translate.goog/index.php/Zone_Humide_d'Ebogo?_x_tr_sl=auto&_x_tr_tl=pt&_x_tr_hl=en&_x_tr_pto=wapp Português]''' | '''[https://wiki-iucnapesportal-org.translate.goog/index.php/Zone_Humide_d'Ebogo?_x_tr_sl=auto&_x_tr_tl=es&_x_tr_hl=en&_x_tr_pto=wapp Español]''' | '''[https://wiki-iucnapesportal-org.translate.goog/index.php/Zone_Humide_d'Ebogo?_x_tr_sl=auto&_x_tr_tl=id&_x_tr_hl=en&_x_tr_pto=wapp Bahasa Indonesia]''' | '''[https://wiki-iucnapesportal-org.translate.goog/index.php/Zone_Humide_d'Ebogo?_x_tr_sl=auto&_x_tr_tl=ms&_x_tr_hl=en&_x_tr_pto=wapp Melayu]''' |
| − | <div style="float: right"> | + | |
| − | {{#display_map: height= | + | __TOC__ |
| − | |3. | + | = Summary = |
| − | }} | + | |
| − | </div> | + | <div style="float: right">{{#display_map: height=190px | width=300px | scrollzoom=off | zoom=5 | layers= OpenStreetMap, OpenTopoMap|3.397017, 11.462335~[[Zone Humide d'Ebogo]]~'Pan troglodytes troglodytes'', ''Gorilla gorilla gorilla''}}</div> |
* Central chimpanzees (''Pan troglodytes troglodytes'') and western lowland gorillas (''Gorilla gorilla gorilla'') are present in Zone Humide d'Ebogo. | * Central chimpanzees (''Pan troglodytes troglodytes'') and western lowland gorillas (''Gorilla gorilla gorilla'') are present in Zone Humide d'Ebogo. | ||
* The population sizes are unknown. | * The population sizes are unknown. | ||
| Line 23: | Line 15: | ||
* The site was designated a Ramsar site in 2012. | * The site was designated a Ramsar site in 2012. | ||
| − | = Site characteristics = | + | |
| + | |||
| + | = Site characteristics = | ||
The site is located about 40 km south of Yaoundé, the capital city of Cameroon. The area supports several IUCN Red-Listed plant species including the African Pearwood (''Baillonella toxisperma''), Sapele (''Entandrophragma cylindricum'') and Ebony (''Diospyros crassiflora''). It also supports nationally important animal species such as the Nile Monitor (''Varanus niloticus'') and the African Python (''Python sebae'') as well as over 100 waterbird species. The temporarily flooded marshes serve as food and breeding ground for waterbirds. It was designated as a Ramsar site in 2012. The forest also supports a rich diversity of non-timber forest products important to the local population both as a source of food and as a cultural heritage ([https://rsis.ramsar.org/fr/ris/2068 Ramsar 2012]). The area is surrounded by the Mbalyamo Forest Reserve. | The site is located about 40 km south of Yaoundé, the capital city of Cameroon. The area supports several IUCN Red-Listed plant species including the African Pearwood (''Baillonella toxisperma''), Sapele (''Entandrophragma cylindricum'') and Ebony (''Diospyros crassiflora''). It also supports nationally important animal species such as the Nile Monitor (''Varanus niloticus'') and the African Python (''Python sebae'') as well as over 100 waterbird species. The temporarily flooded marshes serve as food and breeding ground for waterbirds. It was designated as a Ramsar site in 2012. The forest also supports a rich diversity of non-timber forest products important to the local population both as a source of food and as a cultural heritage ([https://rsis.ramsar.org/fr/ris/2068 Ramsar 2012]). The area is surrounded by the Mbalyamo Forest Reserve. | ||
'''Table 1. Basic site information for Zone Humide d'Ebogo''' | '''Table 1. Basic site information for Zone Humide d'Ebogo''' | ||
| − | {| border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" class=" | + | {| border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" class="Site_characteristics-table" |
| − | | Area | + | |Species |
| + | |'Pan troglodytes troglodytes'', ''Gorilla gorilla gorilla'' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Area | ||
|30.97 km² | |30.97 km² | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Coordinates | |Coordinates | ||
| − | |3. | + | |Lat: 3.397017 , Lon: 11.462335 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Type of site |
| − | |Forest Reserve | + | |Protected area (Forest Reserve) |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |Habitat types | + | |Habitat types |
|Subtropical/tropical swamp forest | |Subtropical/tropical swamp forest | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Type of governance | ||
| + | | | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | = Ape status = | + | [https://www.iucnredlist.org/resources/habitat-classification-scheme IUCN habitat categories] [[Site designations]] |
| + | |||
| + | = Ape status = | ||
| − | '''Table 2. Ape population estimates | + | |
| − | {| border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" class=" | + | |
| − | ! Species | + | '''Table 2. Ape population estimates reported for Zone Humide d'Ebogo''' |
| − | ! Year | + | {| border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" class="Ape_status-table" |
| − | ! | + | !Species |
| − | ! Density estimate [ind./ km²] (95% CI) | + | !Year |
| − | ! | + | !Occurrence |
| − | ! | + | !Encounter or vistation rate (nests/km; ind/day) |
| − | ! | + | !Density estimate [ind./ km²] (95% CI) |
| − | ! Source | + | !Abundance estimate (95% CI) |
| − | ! Comments | + | !Survey area |
| − | ! A.P.E.S. database ID | + | !Sampling method |
| + | !Analytical framework | ||
| + | !Source | ||
| + | !Comments | ||
| + | !A.P.E.S. database ID | ||
|- | |- | ||
|''Pan troglodytes troglodytes'' | |''Pan troglodytes troglodytes'' | ||
| + | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 64: | Line 70: | ||
| | | | ||
|Zone Humide d'Ebogo | |Zone Humide d'Ebogo | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 70: | Line 77: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|''Gorilla gorilla gorilla'' | |''Gorilla gorilla gorilla'' | ||
| + | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 75: | Line 83: | ||
| | | | ||
|Zone Humide d'Ebogo | |Zone Humide d'Ebogo | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 81: | Line 90: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | = Threats = | + | |
| + | = Threats = | ||
| − | '''Table 3. Threats to apes | + | |
| − | {| border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" class=" | + | '''Table 3. Threats to apes reported for Zone Humide d'Ebogo''' |
| − | ! | + | {| border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" class="Threats-table" |
| − | !Specific threats | + | !Category |
| − | !Threat level | + | !Specific threats |
| − | + | !Threat level | |
| − | !Description | + | !Description |
| − | !Year of threat | + | !Year of threat |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |10 Geological events |
| − | | | + | | |
| − | | | + | |Absent |
| | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |12 Other threat |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| + | |Absent | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |2 Agriculture & aquaculture |
| − | | | + | |2.1 Annual & perennial non-timber crops |
| − | | | + | |High (more than 70% of population affected) |
| − | + | |Agriculture is a major cause of forest degradation in and around the site (Liliane et al. 2022). | |
| − | | | + | |Ongoing (2022) |
| − | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |5 | + | |5 Biological resource use |
|5.2 Gathering terrestrial plants | |5.2 Gathering terrestrial plants | ||
| − | |High | + | |High (more than 70% of population affected) |
| − | |||
|Collection of NFTPs for food and medicine (Liliane et al. 2022). | |Collection of NFTPs for food and medicine (Liliane et al. 2022). | ||
|Ongoing (2022) | |Ongoing (2022) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |5 Biological resource use |
|5.3 Logging & wood harvesting | |5.3 Logging & wood harvesting | ||
| − | |High | + | |High (more than 70% of population affected) |
| − | |||
|Wood harvesting (Liliane et al. 2022). | |Wood harvesting (Liliane et al. 2022). | ||
|Ongoing (2022) | |Ongoing (2022) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |1 Residential & commercial development |
| + | |1.1 Residential areas | ||
| + | |Low (up to 30% of population affected) | ||
| + | |Built areas around the eastern and western boundaries of the site (Liliane et al. 2022). | ||
| + | |Ongoing (2022) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |3 Energy production & mining | ||
| | | | ||
|Unknown | |Unknown | ||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |4 Transportation & service corridors |
| | | | ||
|Unknown | |Unknown | ||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |6 Human intrusions & disturbance |
| | | | ||
|Unknown | |Unknown | ||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |7 Natural system modifications |
| | | | ||
|Unknown | |Unknown | ||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |8 Invasive & other problematic species, genes & diseases |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |9 Pollution |
| | | | ||
|Unknown | |Unknown | ||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |11 Climate change & severe weather |
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | |Unknown |
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://www.iucnredlist.org/resources/threat-classification-scheme IUCN Threats list] | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Conservation activities = | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''Table 4. Conservation activities reported for Zone Humide d'Ebogo''' | ||
| + | {| border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" class="Conservation_activities-table" | ||
| + | !Category | ||
| + | !Specific activity | ||
| + | !Description | ||
| + | !Implementing organization(s) | ||
| + | !Year of activity | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |5 Protection & restoration | ||
| + | |5.2 Legally protect ape habitat | ||
| + | |The site is protected internationally as a Ramsar site since 2012, but the management plan and national authority for the site are unknown (UNEP-WCMC 2023). | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | |Ongoing (2023) |
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Conservation activities list (Junker et al. 2017)]] | |
| + | |||
| + | = Challenges = | ||
| + | |||
| − | '''Table | + | |
| − | {| border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" class=" | + | '''Table 5. Challenges reported for Zone Humide d'Ebogo''' |
| − | ! | + | {| border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" class="Challenges-table" |
| − | !Specific | + | !Challenges |
| − | ! | + | !Specific challenges |
| − | !Year | + | !Source |
| + | !Year(s) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | |
|Not reported | |Not reported | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | = Enablers = | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''Table 6. Enablers reported for Zone Humide d'Ebogo''' | ||
| + | {| border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" class="enabler-table" | ||
| + | !Enablers | ||
| + | !Specific enablers | ||
| + | !Source | ||
| + | !Year(s) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |1 Site management |
| − | | | + | | |
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |2 Resources and capacity |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |3 Engaged community |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |4 Institutional support |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |5 Ecological context |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |6 Safety and stability |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | = Research activities = | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | = Documented behaviours = | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | '''Table | + | '''Table 7. Behaviours documented for Zone Humide d'Ebogo''' |
| − | {| border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" class=" | + | {| border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" class="behaviours-table" |
| − | ! | + | !Behavior |
!Source | !Source | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Not reported | |Not reported | ||
| | | | ||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
= Exposure to climate change impacts = | = Exposure to climate change impacts = | ||
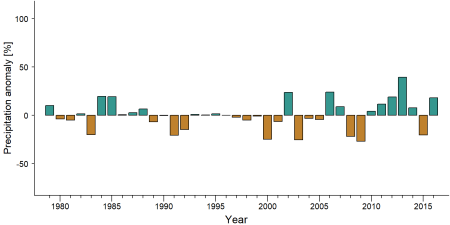
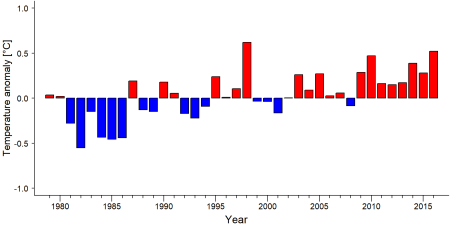
As part of a study on the exposure of African great ape sites to climate change impacts, Kiribou et al. subm. extracted climate data and data on projected extreme climate impact events for the site. Climatological characteristics were derived from observation-based climate data provided by the Inter-Sectoral Impact Model Intercomparison Project (ISIMIP, www.isimip.org). Parameters were calculated as the average across each 30-year period. For 1981-2010, the EWEMBI dataset from ISIMIP2a was used. For the two future periods (2021-2050 and 2071-2099) ISIMIP2b climate data based on four CMIP5 global climate models were used. For future projections, two Representative Concentration Pathways (RCP) were used. RCP 2.6 is a scenario with strong mitigation measures in which global temperatures would likely rise below 2°C. RCP 6.0 is a scenario with medium emissions in which global temperatures would likely rise up to 3°C by 2100. For the number of days with heavy precipitation events, the 98th percentile of all precipitation days (>1mm/d) was calculated for the 1979-2013 reference period as a threshold for a heavy precipitation event. Then, for each year, the number of days above that threshold was derived. The figures on temperature and precipitation anomaly show the deviation from the mean temperature and mean precipitation for the 1979-2013 reference period. | As part of a study on the exposure of African great ape sites to climate change impacts, Kiribou et al. subm. extracted climate data and data on projected extreme climate impact events for the site. Climatological characteristics were derived from observation-based climate data provided by the Inter-Sectoral Impact Model Intercomparison Project (ISIMIP, www.isimip.org). Parameters were calculated as the average across each 30-year period. For 1981-2010, the EWEMBI dataset from ISIMIP2a was used. For the two future periods (2021-2050 and 2071-2099) ISIMIP2b climate data based on four CMIP5 global climate models were used. For future projections, two Representative Concentration Pathways (RCP) were used. RCP 2.6 is a scenario with strong mitigation measures in which global temperatures would likely rise below 2°C. RCP 6.0 is a scenario with medium emissions in which global temperatures would likely rise up to 3°C by 2100. For the number of days with heavy precipitation events, the 98th percentile of all precipitation days (>1mm/d) was calculated for the 1979-2013 reference period as a threshold for a heavy precipitation event. Then, for each year, the number of days above that threshold was derived. The figures on temperature and precipitation anomaly show the deviation from the mean temperature and mean precipitation for the 1979-2013 reference period. | ||
| + | |||
The estimated exposure to future extreme climate impact events (crop failure, drought, river flood, wildfire, tropical cyclone, and heatwave) is based on a published dataset by Lange et al. 2020 derived from ISIMIP2b data. The same global climate models and RCPs as described above were used. Within each 30-year period, the number of years with an extreme event and the average proportion of the site affected were calculated (see Kiribou et al. subm. for details). | The estimated exposure to future extreme climate impact events (crop failure, drought, river flood, wildfire, tropical cyclone, and heatwave) is based on a published dataset by Lange et al. 2020 derived from ISIMIP2b data. The same global climate models and RCPs as described above were used. Within each 30-year period, the number of years with an extreme event and the average proportion of the site affected were calculated (see Kiribou et al. subm. for details). | ||
| − | '''Table | + | '''Table 8. Estimated past and projected climatological characteristics in Zone Humide d'Ebogo''' |
| − | {| border= | + | {| border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" class="clima-table" |
| − | + | !'''Value''' | |
| − | + | !'''1981-2010''' | |
| − | + | !'''2021-2050, RCP 2.6''' | |
| − | + | !'''2021-2050, RCP 6.0''' | |
| − | + | !'''2071-2099, RCP 2.6''' | |
| − | + | !'''2071-2099, RCP 6.0''' | |
|- | |- | ||
|Mean temperature [°C] | |Mean temperature [°C] | ||
| Line 331: | Line 327: | ||
|8.5 | |8.5 | ||
|9.5 | |9.5 | ||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
| − | '''Table | + | '''Table 9. Projected exposure of apes to extreme climate impact events in Zone Humide d'Ebogo''' |
| − | {| border= | + | {| border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" class="clima2-table" |
| − | + | !'''Type''' | |
| − | + | !'''No. of years with event (2021-2050, RCP 2.6)''' | |
| − | + | !'''% of site exposed (2021-2050, RCP 2.6)''' | |
| − | + | !'''No. of years with event (2021-2050, RCP 6.0)''' | |
| − | + | !'''% of site exposed (2021-2050, RCP 6.0)''' | |
| − | + | !'''No. of years with event (2070-2099, RCP 2.6)''' | |
| − | + | !'''% of site exposed (2070-2099, RCP 2.6)''' | |
| − | + | !'''No. of years with event (2070-2099, RCP 6.0)''' | |
| − | + | !'''% of site exposed (2070-2099, RCP 6.0)''' | |
|- | |- | ||
|Crop failure | |Crop failure | ||
| Line 406: | Line 401: | ||
|29 | |29 | ||
|0.33 | |0.33 | ||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | =External links= | + | <div><ul><li style="display: inline-block; vertical-align: top;"> [[File: PrecipAnomaly Zone Humide d Ebogo.png | 450px | thumb| right | Precipitation anomaly in Zone Humide d'Ebogo]] </li><li style="display: inline-block; vertical-align: top;"> [[File: TempAnomaly Zone Humide d Ebogo.png | 450px | thumb| right | Temperature anomaly in Zone Humide d'Ebogo]] </li></ul></div> |
| + | |||
| + | = External links = | ||
| + | |||
[https://rsis.ramsar.org/fr/ris/2068 Ramsar] | [https://rsis.ramsar.org/fr/ris/2068 Ramsar] | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Relevant datasets = | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
= References = | = References = | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Kiribou, R., Tehoda, P., Chukwu, O., Bempah, G., Kühl, H.S., Ferreira, J., Sop, T., Carvalho, J., Mengel, M., Heinicke, S. (subm) Exposure of African ape sites to climate change impacts. | |
| − | '''Page | + | |
| + | Liliane, M. D., Romain, N. J., Caroline, M. S. M., Abigaelle, T., & Loic, T. T. A. (2022). Quantifying Forest Loss in the Mbalmayo Forest Reserve (Center Region, Cameroon). Journal of Geoscience and Environment Protection, 10(9), 271-288. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Ramsar (2012. Zone Humide d'Ebogo. Online: https://rsis.ramsar.org/fr/ris/2068 | ||
| + | |||
| + | UNEP-WCMC (2023). Protected Area Profile for Zone Humide d'Ebogo from the World Database on Protected Areas, May 2023. Available at: www.protectedplanet.net | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''Page created by: '''A.P.E.S. Wiki team''' Date:''' NA | ||
Latest revision as of 05:31, 19 March 2025
Central Africa > Cameroon > Zone Humide d'Ebogo
Français | Português | Español | Bahasa Indonesia | Melayu
Summary
- Central chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes troglodytes) and western lowland gorillas (Gorilla gorilla gorilla) are present in Zone Humide d'Ebogo.
- The population sizes are unknown.
- The population trends are unknown.
- The site has a total size of 30.97 km².
- Forest loss and forest degradation due to wood harvesting, agriculture and collection of non-timber forest products are some of the known threats in the site.
- Conservation activities are unknown.
- The site was designated a Ramsar site in 2012.
Site characteristics
The site is located about 40 km south of Yaoundé, the capital city of Cameroon. The area supports several IUCN Red-Listed plant species including the African Pearwood (Baillonella toxisperma), Sapele (Entandrophragma cylindricum) and Ebony (Diospyros crassiflora). It also supports nationally important animal species such as the Nile Monitor (Varanus niloticus) and the African Python (Python sebae) as well as over 100 waterbird species. The temporarily flooded marshes serve as food and breeding ground for waterbirds. It was designated as a Ramsar site in 2012. The forest also supports a rich diversity of non-timber forest products important to the local population both as a source of food and as a cultural heritage (Ramsar 2012). The area is surrounded by the Mbalyamo Forest Reserve.
Table 1. Basic site information for Zone Humide d'Ebogo
| Species | 'Pan troglodytes troglodytes, Gorilla gorilla gorilla |
| Area | 30.97 km² |
| Coordinates | Lat: 3.397017 , Lon: 11.462335 |
| Type of site | Protected area (Forest Reserve) |
| Habitat types | Subtropical/tropical swamp forest |
| Type of governance |
IUCN habitat categories Site designations
Ape status
Table 2. Ape population estimates reported for Zone Humide d'Ebogo
| Species | Year | Occurrence | Encounter or vistation rate (nests/km; ind/day) | Density estimate [ind./ km²] (95% CI) | Abundance estimate (95% CI) | Survey area | Sampling method | Analytical framework | Source | Comments | A.P.E.S. database ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pan troglodytes troglodytes | Zone Humide d'Ebogo | Unknown | |||||||||
| Gorilla gorilla gorilla | Zone Humide d'Ebogo | Unknown |
Threats
Table 3. Threats to apes reported for Zone Humide d'Ebogo
| Category | Specific threats | Threat level | Description | Year of threat |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 Geological events | Absent | |||
| 12 Other threat | Absent | |||
| 2 Agriculture & aquaculture | 2.1 Annual & perennial non-timber crops | High (more than 70% of population affected) | Agriculture is a major cause of forest degradation in and around the site (Liliane et al. 2022). | Ongoing (2022) |
| 5 Biological resource use | 5.2 Gathering terrestrial plants | High (more than 70% of population affected) | Collection of NFTPs for food and medicine (Liliane et al. 2022). | Ongoing (2022) |
| 5 Biological resource use | 5.3 Logging & wood harvesting | High (more than 70% of population affected) | Wood harvesting (Liliane et al. 2022). | Ongoing (2022) |
| 1 Residential & commercial development | 1.1 Residential areas | Low (up to 30% of population affected) | Built areas around the eastern and western boundaries of the site (Liliane et al. 2022). | Ongoing (2022) |
| 3 Energy production & mining | Unknown | |||
| 4 Transportation & service corridors | Unknown | |||
| 6 Human intrusions & disturbance | Unknown | |||
| 7 Natural system modifications | Unknown | |||
| 8 Invasive & other problematic species, genes & diseases | Unknown | |||
| 9 Pollution | Unknown | |||
| 11 Climate change & severe weather | Unknown |
Conservation activities
Table 4. Conservation activities reported for Zone Humide d'Ebogo
| Category | Specific activity | Description | Implementing organization(s) | Year of activity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 Protection & restoration | 5.2 Legally protect ape habitat | The site is protected internationally as a Ramsar site since 2012, but the management plan and national authority for the site are unknown (UNEP-WCMC 2023). | Ongoing (2023) |
Conservation activities list (Junker et al. 2017)
Challenges
Table 5. Challenges reported for Zone Humide d'Ebogo
| Challenges | Specific challenges | Source | Year(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Not reported |
Enablers
Table 6. Enablers reported for Zone Humide d'Ebogo
| Enablers | Specific enablers | Source | Year(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Site management | |||
| 2 Resources and capacity | |||
| 3 Engaged community | |||
| 4 Institutional support | |||
| 5 Ecological context | |||
| 6 Safety and stability |
Research activities
Documented behaviours
Table 7. Behaviours documented for Zone Humide d'Ebogo
| Behavior | Source |
|---|---|
| Not reported |
Exposure to climate change impacts
As part of a study on the exposure of African great ape sites to climate change impacts, Kiribou et al. subm. extracted climate data and data on projected extreme climate impact events for the site. Climatological characteristics were derived from observation-based climate data provided by the Inter-Sectoral Impact Model Intercomparison Project (ISIMIP, www.isimip.org). Parameters were calculated as the average across each 30-year period. For 1981-2010, the EWEMBI dataset from ISIMIP2a was used. For the two future periods (2021-2050 and 2071-2099) ISIMIP2b climate data based on four CMIP5 global climate models were used. For future projections, two Representative Concentration Pathways (RCP) were used. RCP 2.6 is a scenario with strong mitigation measures in which global temperatures would likely rise below 2°C. RCP 6.0 is a scenario with medium emissions in which global temperatures would likely rise up to 3°C by 2100. For the number of days with heavy precipitation events, the 98th percentile of all precipitation days (>1mm/d) was calculated for the 1979-2013 reference period as a threshold for a heavy precipitation event. Then, for each year, the number of days above that threshold was derived. The figures on temperature and precipitation anomaly show the deviation from the mean temperature and mean precipitation for the 1979-2013 reference period.
The estimated exposure to future extreme climate impact events (crop failure, drought, river flood, wildfire, tropical cyclone, and heatwave) is based on a published dataset by Lange et al. 2020 derived from ISIMIP2b data. The same global climate models and RCPs as described above were used. Within each 30-year period, the number of years with an extreme event and the average proportion of the site affected were calculated (see Kiribou et al. subm. for details).
Table 8. Estimated past and projected climatological characteristics in Zone Humide d'Ebogo
| Value | 1981-2010 | 2021-2050, RCP 2.6 | 2021-2050, RCP 6.0 | 2071-2099, RCP 2.6 | 2071-2099, RCP 6.0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean temperature [°C] | 23.8 | 25 | 24.9 | 25.2 | 26.2 |
| Annual precipitation [mm] | 2228 | 2308 | 2326 | 2389 | 2375 |
| Max no. consecutive dry days (per year) | 28.6 | 17.3 | 18.5 | 15.3 | 21.4 |
| No. days with heavy precipitation (per year) | 6 | 7.8 | 8.1 | 8.5 | 9.5 |
Table 9. Projected exposure of apes to extreme climate impact events in Zone Humide d'Ebogo
| Type | No. of years with event (2021-2050, RCP 2.6) | % of site exposed (2021-2050, RCP 2.6) | No. of years with event (2021-2050, RCP 6.0) | % of site exposed (2021-2050, RCP 6.0) | No. of years with event (2070-2099, RCP 2.6) | % of site exposed (2070-2099, RCP 2.6) | No. of years with event (2070-2099, RCP 6.0) | % of site exposed (2070-2099, RCP 6.0) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crop failure | 7 | 1.3 | 4.5 | 1.28 | 4.5 | 0.78 | 16.5 | 0.96 |
| Drought | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Heatwave | 0 | 0 | 0.5 | 50 | 2.5 | 100 | 2 | 100 |
| River flood | 1 | 0.35 | 2 | 4.69 | 0.5 | 2.76 | 3 | 0.84 |
| Tropical cyclone | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Wildfire | 30 | 0.27 | 30 | 0.3 | 29 | 0.28 | 29 | 0.33 |
External links
Relevant datasets
References
Kiribou, R., Tehoda, P., Chukwu, O., Bempah, G., Kühl, H.S., Ferreira, J., Sop, T., Carvalho, J., Mengel, M., Heinicke, S. (subm) Exposure of African ape sites to climate change impacts.
Liliane, M. D., Romain, N. J., Caroline, M. S. M., Abigaelle, T., & Loic, T. T. A. (2022). Quantifying Forest Loss in the Mbalmayo Forest Reserve (Center Region, Cameroon). Journal of Geoscience and Environment Protection, 10(9), 271-288.
Ramsar (2012. Zone Humide d'Ebogo. Online: https://rsis.ramsar.org/fr/ris/2068
UNEP-WCMC (2023). Protected Area Profile for Zone Humide d'Ebogo from the World Database on Protected Areas, May 2023. Available at: www.protectedplanet.net
Page created by: A.P.E.S. Wiki team Date: NA