Cao Vit Gibbon Conservation Area
Asia > Vietnam > Cao Vit Gibbon Conservation Area
Français | Português | Español | Bahasa Indonesia | Melayu
Summary






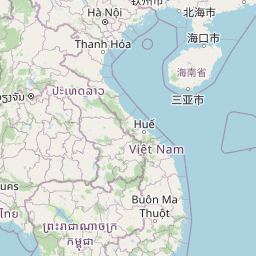

- Eastern Black Gibbons (Nomascus nasutus) are present in Cao Vit Gibbon Conservation Area.
- It has been estimated that 100-130 individuals occur in the site.
- The gibbon population trend is stable.
- The site has a total size of 16.56 km².
- Key threats to gibbons are habitat degradation, timber extraction.
- Conservation activities have focused on education and awareness raising, and regular patrols.
Site characteristics
The Cao Vit Gibbon Conservation Area is located in the Trung Khanh District, Cao Bang Province, Vietnam, bordering China. The population is believed to be confined to this area and therefore is of high international and national importance for gibbon conservation. The population was rediscovered by FFI Vietnamese scientists in 2002 in a small fragmented forest (Rawson et al. 2011).
Table 1. Basic site information for Cao Vit Gibbon Conservation Area
| Species | 'Nomascus nasutus |
| Area | 16.56 km² |
| Coordinates | Lat: 22.883148 , Lon: 106.704305 |
| Type of site | Conservation area |
| Habitat types | Subtropical/tropical moist montane forest |
| Type of governance |
IUCN habitat categories Site designations
Ape status
Gibbons were first recorded in the area in 2002. In 2007 a gibbon census recorded 17 groups of 94 to 96 individuals; including the groups in China, the total population was estimated at 18 groups of 110 individuals (Rawson et al. 2011). In 2009 Chinese researchers in Jingxi County, Guangxi Province observed the formation of a new group along the border. Other gibbons surveys have been conducted in 2007, 2006, and 2002, however, due to differing survey efforts, objectives (e.g. training local patrol staff, rapid assessment), seasonal variation, survey results cannot be directly compared. Nevertheless, the population trend is increasing (Rawson et al. 2011).
Table 2. Ape population estimates reported for Cao Vit Gibbon Conservation Area
| Species | Year | Total number indiv. (95% CI) | Total number groups (95% CI) | Density [groups/km²] (95% CI) | Area | Method | Source | Comments | A.P.E.S. database ID | NA | NA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nomascus nasutus | 2002 | 5 | 26-28 | Cao Vit Gibbon Conservation Area | Unknown | Geissmann et al. 2002 |
Threats
The small size of the site, limited extent of gibbon habitat and ongoing (but decreasing) degradation of habitat are the main threats to gibbons. Local communities extract timber from the site for fuelwood, waterwheels, house construction and other domestic use, and they collect non-timber forest products and food for livestock. Due to their small population size, gibbons are vulnerable to stochastic events such as fire, disease or reduced gene flow. In addition, climate change may impact the extent and composition of remaining gibbon habitat (Rawson et al. 2011).
Table 3. Threats to apes reported for Cao Vit Gibbon Conservation Area
| Category | Specific threats | Threat level | Description | Year of threat |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 Geological events | Absent | |||
| 12 Other threat | Absent | |||
| 5 Biological resource use | 5.2 Gathering terrestrial plants | Present (unknown severity) | Collection of non-timber forest products and food for livestock (Rawson et al. 2011). | Ongoing (2011) |
| 5 Biological resource use | 5.3 Logging & wood harvesting | Present (unknown severity) | Extraction of timber for fuelwood, waterwheels, house construction and other domestic use (Rawson et al. 2011). | Ongoing (2011) |
| 1 Residential & commercial development | Unknown | |||
| 2 Agriculture & aquaculture | Unknown | |||
| 3 Energy production & mining | Unknown | |||
| 4 Transportation & service corridors | Unknown | |||
| 6 Human intrusions & disturbance | Unknown | |||
| 7 Natural system modifications | Unknown | |||
| 8 Invasive & other problematic species, genes & diseases | Unknown | |||
| 9 Pollution | Unknown | |||
| 11 Climate change & severe weather | Unknown |
Conservation activities
The Cao Vit Gibbon Conservation Area was designated in Trung Khanh District in 2007. In 2009 a contiguous nature reserve was designated in Jingxi County, China. FFI has worked with local government agencies and communities in both Trung Khanh District and Jingxi County since 2003 and 2006 respectively (Rawson et al. 2011).
Table 4. Conservation activities reported for Cao Vit Gibbon Conservation Area
| Category | Specific activity | Description | Implementing organization(s) | Year of activity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 Counter-wildlife crime | 2.3 Conduct regular anti-poaching patrols | With support from IUCN SOS Gibbons, FFI and the FPD conduct regular patrols to protect the gibbon population and the conservation area (Ali, N. 2022). | Ongoing (2022) | |
| 2 Counter-wildlife crime | 2.11 Implement monitoring surveillance strategies (e.g., SMART) or use monitoring data to improve effectiveness of patrols | During patrols the rangers collect data using the Spatial Monitoring and Reporting Tool (SMART) (Ali, N. 2022). | Ongoing (2022) |
Conservation activities list (Junker et al. 2017)
Challenges
Table 5. Challenges reported for Cao Vit Gibbon Conservation Area
| Challenges | Specific challenges | Source | Year(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Not reported |
Enablers
Table 6. Enablers reported for Cao Vit Gibbon Conservation Area
| Enablers | Specific enablers | Source | Year(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Site management | |||
| 2 Resources and capacity | |||
| 3 Engaged community | |||
| 4 Institutional support | |||
| 5 Ecological context | |||
| 6 Safety and stability |
Research activities
The Cao-vit Gibbon Conservation Team, which consists of 11 members including government staff and people from local communities, conduct regular monitoring of the gibbon population in the conservation area. A novel method being piloted in the area is acoustic monitoring. FFI has deployed 50 audio moths across the entire range of the gibbon population in the conservation area. Data collected by these devices will help to improve the accuracy of population survey and monitoring results (Ali, N. 2022).
Documented behaviours
Table 7. Behaviours documented for Cao Vit Gibbon Conservation Area
| Behavior | Source |
|---|---|
| Not reported |
Exposure to climate change impacts
External links
Relevant datasets
References
Ali, Noor (Dec 06, 2022). Saving the Cao-vit Gibbon in northern Vietnam. Online: https://www.iucn.org/blog/202212/saving-cao-vit-gibbon-northern-vietnam
Rawson, B. M, Insua-Cao, P., Nguyen Manh Ha, Van Ngoc Thinh, Hoang Minh Duc, Mahood, S., Geissmann, T. and Roos, C. 2011. The Conservation Status of Gibbons in Vietnam. Fauna & Flora International/Conservation International, Hanoi, Vietnam
Page created by: A.P.E.S. Wiki team Date: NA