Bia Conservation Area
West Africa > Ghana > Bia Conservation Area
Français | Português | Bahasa Indonesia | Melayu
Summary
- Western chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes verus) are present in the Bia Conservation Area.
- The population size is estimated at 34 weaned individuals.
- The chimpanzee population trend is decreasing.
- The site has a total size of 306 km².
- Illegal hunting is the main threat.
- Conservation activities have focused on anti-poaching patrols.
Site characteristics
The Bia Conservation Area (BCA) forms a 306 km² block in the moist evergreen and moist semi-deciduous forest zones of western Ghana, between the Bia River and the border with Côte d’Ivoire. BCA encompasses Bia National Park and Bia Resource Reserve; Bia National Park is 78 km² and Bia Resource Reserve is 228 km². The BCA was originally part of a larger (about 1500 km²) ecosystem for forest elephants known as the Bia Group of Forest Reserves. However, the Bia elephant range has reduced over time due to clearance for cocoa cultivation, and is now an isolated population in an ecological island of forest with hard boundaries and no transitional zone to farmland (PADP 2001). It is planned for the entire area to be upgraded to national park status (Quansah P. K., pers. comm. 2023).
Table 1. Basic site information for Bia Conservation Area
| Species | Pan troglodytes verus |
| Area | 306 km² |
| Coordinates | 6.481132, -3.112847 |
| Type of site | Conservation area (national park, resource reserve) |
| Governance type | |
| Habitat type | Subtropical/tropical moist lowland forest |
Types of sites ⋅ Governance types ⋅ Habitat types
Ape status
Wildlife patrol team encounters with chimpanzee signs indicate a decreasing trend (Danquah, E., pers. comm. 2022).
Table 2. Ape population estimates in Bia Conservation Area
| Species | Year | Occurrence | Encounter or visitation rate (nests/km; ind/day) | Density estimate [ind/ km²] (95% CI) | Abundance estimate (95% CI) | Survey area | Sampling method | Analytical framework | Source | Comments | A.P.E.S. database ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pan troglodytes verus | 2019-2020 | Present | 34 | Bia Conservation Area (306 km²) | Line transects | Ofori-Amanfo, R. pers comm. 2023 | Estimate for weaned individuals |
Sampling methods ⋅ Analytical frameworks
Threats
A total of 3,721 illegal human signs which are threats to the subspecies were recorded in 2021 and provided an overall encounter rate of 5.69 human signs per a kilometre walk. Three major threats among these were cartridge case (45.9%), wire snare (29.4%) and illegal logging (14.2%) (Danquah, E., pers. comm. 2022). Poachers still hunt in the park and set snares that also affect chimpanzees. Although poaching is not very frequent, it is a main threat because of the site’s low chimpanzee population abundance. Farm raids by wildlife resulting in human-wildlife conflict with elephants the most, but chimpanzees are also involved; with chimpanzees being low in numbers compared to elephants, it means a major threat to the chimpanzee population (Quansah P. K., pers. comm. 2023).
Table 3. Threats to apes in Bia Conservation Area
| Category | Specific threats | Threat level | Description | Year of threat |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Residential & commercial development | Unknown | |||
| 2. Agriculture & aquaculture | 2.1 Annual & perennial non-timber crops | Low | Habitat encroachment due to agriculture (Quansah P. K., pers. comm. 2023). | 1974-Ongoing (2023) |
| 3. Energy production & mining | Unknown | |||
| 4. Transportation & service corridors | Unknown | |||
| 5. Biological resource use | 5.1 Hunting & collecting terrestrial animals | Medium | Cartridge cases and wire snares (Danquah, E. pers. comm. 2022). Poaching of wildlife which includes illegal entry with guns to kill wildlife and setting of traps like wire snares (Quansah P. K., pers. comm. 2023). | 1935-Ongoing (2023) |
| 6. Human intrusion & disturbance | Unknown | |||
| 7. Natural system modifications | 7.1 Fire & fire suppression | Low | Hunting for tree Hyrax with the use of fires, resulting sometimes in bushfires (Quansah P. K., pers. comm. 2023). | 1935-Ongoing (2023) |
| 8. Invasive & other problematic species, genes, diseases | Unknown | |||
| 9. Pollution | Unknown | |||
| 10. Geological Events | Absent | |||
| 11. Climate change & severe weather | Unknown | |||
| 12. Other options | Absent |
Conservation activities
Bia Conservation Area is a protected area so there are dedicated staff who patrol inside the Park to protect the resources including the chimpanzees. There is also a community outreach team that goes to the communities to educate them about the need to conserve natural resources including the chimpanzees. Ghana's Wildlife Division is responsible for maintaining law and order within the protected area. Between February and September 2023, the park conducted a programme, with funding from the Africa Elephant Fund (AEF), in 11 human wildlife hotspot communities where wildlife (with emphasis on elephants) invade community farms and livelihoods resulting in human wildlife conflict situations sometimes resulting in reprisal killings of wildlife. These communities were sensitised and educated on ways to mitigate human wildlife conflicts. Community Volunteer Squads were then formed, trained and given implements and the necessary tools and education to prevent wildlife raids on farms which results in human wildlife conflicts (Quansah P. K., pers. comm. 2023).
Table 4. Conservation activities in Bia Conservation Area
| Category | Specific activity | Description | Implementing organization | Year of activity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Development impact mitigation | Not reported | |||
| 2. Counter-wildlife crime | 2.3 Conduct regular anti-poaching patrols | Wildlife patrol teams regularly conduct law enforcement duties within and around the protected area (Danquah, E., 2022). Anti-poaching operations (day, night and long patrols) (Ofori-Amanfo pers. obs. 2023). | 1974-Ongoing (2023) | |
| 3. Species health | Not reported | |||
| 4. Education & awareness | 4.1 Educate local communities about apes and sustainable use | Conservation education and outreach programmes in communities around the Park (Ofori-Amanfo pers. obs. 2023). | 2000-Ongoing (2023) | |
| 4. Education & awareness | 4.2 Involve local community in ape research and conservation management | Communities around the park are aggregated into 10 Community Resource Management Areas (CREMAs) where they have a constitution and management plans backed by the local government to regulate the use of their natural resources and also help protect the protected area from human entering (Quansah P. K., pers. comm. 2023). | 1974-Ongoing (2023) | |
| 5. Protection & restoration | 5.2 Legally protect ape habitat | 1935-Ongoing (2023) | ||
| 5. Protection & restoration | 5.5 Demarcate and enforce boundaries of protected areas | Fifty (50) missing, broken and defaced boundary pillars were replaced (out of a total of 115 boundary pillar points identified) to properly demarcate and delineate the park from fringe farms and prevent encroachment into the park (Quansah P. K., pers. comm. 2023). | 2020 | |
| 5. Protection & restoration | 5.6 Habitat restoration | Enrichment planting has been carried out with some different kinds of indigenous tree species in some degraded portions of the Resource Reserve. The entire Bia Conservation Area boundary has been planted with indigenous tree species to prevent encroachment into the Park (Ofori-Amanfo pers. obs. 2023, Quansah P. K., pers. comm. 2023). | 2018-2022 | |
| 6. Species management | Not reported | |||
| 7. Economic & other incentives | 7.1 Provide monetary benefits to local communities for sustainably managing their forest and its wildlife (e.g., REDD, alternative income, employment) | The park has been employing community people around the park as staff since the park was established in 1974 up till now. In the last 5 years the park has employed about 10 people in communities surrounding the park (Quansah P. K., pers. comm. 2023). | 1974-Ongoing (2023) | |
| 7. Economic & other incentives | 7.2 Provide non-monetary benefits to local communities for sustainably managing their forest and its wildlife (e.g., better education, infrastructure development) | Provision of school and other infrastructural development (Quansah P. K., pers. comm. 2023). | 1974-Ongoing (2023) | |
| 7. Economic & other incentives | 7.2 Provide non-monetary benefits to local communities for sustainably managing their forest and its wildlife (e.g., better education, infrastructure development) | Tropenbos Ghana, UNESCO, NCRC, and SNV Ghana support income generating activities such as beekeeping and honey processing, palm oil processing, soap production, snail farming, and mushroom cultivation (Quansah P. K., pers. comm. 2023). | 1993-Ongoing (2023) | |
| 8. Permanent presence | Not reported |
Conservation implementation challenges and enablers
The Ghana Wildlife Division has few staff and resources to conduct effective and regular anti-poaching activities within and around the protected area. Inadequate staff, field equipment, vehicles etc. hinder effective protection of the chimpanzees.
Table 5. Challenges reported for Bia Conservation Area
| Category | Challenge | Source | Year(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Site management | Outdated management plan | Quansah P. K., pers. comm. 2023 | |
| 2. Resources & capacity | 2.5 Lack of equipment/transportation | Quansah P. K., pers. comm. 2023 | |
| 2. Resources & capacity | 2.7 Lack of infrastructure | Quansah P. K., pers. comm. 2023 | |
| 2. Resources & capacity | 2.2 Lack of staff | Quansah P. K., pers. comm. 2023 | |
| 2. Resources & capacity | 2.3 General lack of funding | Quansah P. K., pers. comm. 2023 | |
| 2. Resources & capacity | 2.6 Lack of biomonitoring/survey data | Quansah P. K., pers. comm. 2023 | |
| 3. Engaged community | Not reported | ||
| 4. Institutional support | Not reported | ||
| 5. Ecological context | Not reported | ||
| 6. Safety & stability | Not reported |
Table 6. Enablers reported for Bia Conservation Area
| Category | Enabler | Source | Year(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Site management | Not reported | ||
| 2. Resources & capacity | Not reported | ||
| 3. Engaged community | Not reported | ||
| 4. Institutional support | Not reported | ||
| 5. Ecological context | Not reported | ||
| 6. Safety & stability | Not reported |
Research activities
Bia Conservation Area is part of the Pan African Programme: The Cultured Chimpanzee (PanAf).
Documented behaviours
Table 7. Ape behaviors reported for Bia Conservation Area
| Behavior | Source |
|---|---|
| Not reported |
Exposure to climate change impacts
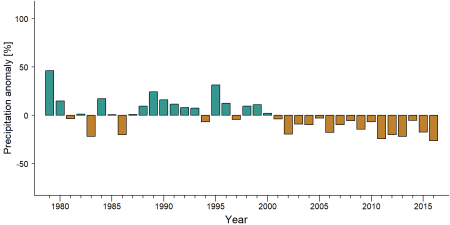
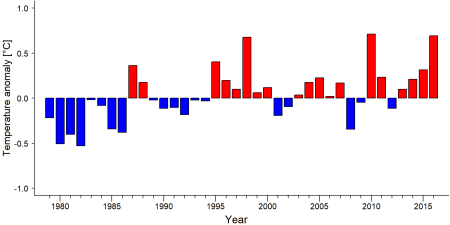
As part of a study on the exposure of African great ape sites to climate change impacts, Kiribou et al. (2024) extracted climate data and data on projected extreme climate impact events for the site. Climatological characteristics were derived from observation-based climate data provided by the Inter-Sectoral Impact Model Intercomparison Project ([ISIMIP www.isimip.org]). Parameters were calculated as the average across each 30-year period. For future projections, two Representative Concentration Pathways (RCP) were used. RCP 2.6 is a scenario with strong mitigation measures in which global temperatures would likely rise below 2°C. RCP 6.0 is a scenario with medium emissions in which global temperatures would likely rise up to 3°C by 2100. For the number of days with heavy precipitation events, the 98th percentile of all precipitation days (>1mm/d) was calculated for the 1979-2013 reference period as a threshold for a heavy precipitation event. Then, for each year, the number of days above that threshold was derived. The figures on temperature and precipitation anomaly show the deviation from the mean temperature and mean precipitation for the 1979-2013 reference period. The estimated exposure to future extreme climate impact events (crop failure, drought, river flood, wildfire, tropical cyclone, and heatwave) is based on a published dataset by Lange et al. 2020 derived from ISIMIP2b data. The same global climate models and RCPs as described above were used. Within each 30-year period, the number of years with an extreme event and the average proportion of the site affected were calculated (Kiribou et al. 2024).
Table 8. Estimated past and projected climatological characteristics in Bia Conservation Area
| 1981-2010 | 2021-2050, RCP 2.6 | 2021-2050, RCP 6.0 | 2071-2099, RCP 2.6 | 2071-2099, RCP 6.0 | |
| Mean temperature [°C] | 27 | 28.1 | 27.9 | 28.2 | 29.4 |
| Annual precipitation [mm] | 1295 | 1253 | 1314 | 1258 | 1335 |
| Max no. consecutive dry days (per year) | 28.9 | 26.1 | 28.8 | 30.3 | 30.6 |
| No. days with heavy precipitation (per year) | 6.5 | 6.1 | 6.5 | 5.8 | 8.3 |
Table 9. Projected exposure of apes to extreme climate impact events in Bia Conservation Area
| No. of years with event (2021-2050, RCP 2.6) | % of site exposed (2021-2050, RCP 2.6) | No. of years with event (2021-2050, RCP 6.0) | % of site exposed (2021-2050, RCP 6.0) | No. of years with event (2070-2099, RCP 2.6) | % of site exposed (2070-2099, RCP 2.6) | No. of years with event (2070-2099, RCP 6.0) | % of site exposed (2070-2099, RCP 6.0) | |
| Crop failure | 6.5 | 3.41 | 3.5 | 2.27 | 3.5 | 3.41 | 12 | 3.41 |
| Drought | 1.5 | 50 | 0.5 | 50 | 1.25 | 50 | 0 | 0 |
| Heatwave | 8 | 100 | 7.5 | 100 | 8.5 | 100 | 2.5 | 100 |
| River flood | 0.75 | 0.09 | 1.5 | 1.03 | 2.25 | 1.66 | 0.75 | 0.85 |
| Tropical cyclone | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Wildfire | 30 | 0.44 | 30 | 0.42 | 29 | 0.44 | 29 | 0.46 |
External links
References
Kiribou, R., Tehoda, P., Chukwu, O., Bempah, G., Kühl, H. S., Ferreira, J., ... & Heinicke, S. (2024). Exposure of African ape sites to climate change impacts. PLOS Climate, 3(2), e0000345.
Lange, S., Volkholz, J., Geiger, T., Zhao, F., Vega, I., Veldkamp, T., ... & Frieler, K. (2020). Projecting exposure to extreme climate impact events across six event categories and three spatial scales. Earth's Future, 8(12), e2020EF001616.
Cite as: Danquah, E., Ofori-Amanfo, R. & Papa Kwaw Quansah (2023) Bia Conservation Area. A.P.E.S. Wiki. Retrieved Month Day, Year, from https://wiki.iucnapesportal.org/index.php/Bia_Conservation_Area
Page completed by: Emmanuel Danquah, Richard Ofori-Amanfo & Papa Kwaw Quansah Date: 17/11/2023